Your smile is the number one thing people notice upon meeting you. And a confident smile can boost your self-esteem and confidence. But some situations like tooth loss and receding gum can affect that. It’s best to know how to deal with it early on before it escalates.
Gum disease is a common and often underdiagnosed condition that affects the gums and bones supporting the teeth. If left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss, pain, and a host of other oral health issues.
The good news is that gum disease is preventable and treatable, and with the proper care and attention, it’s possible to maintain healthy gums and a beautiful smile. This post will explore the causes of gum disease, its symptoms, and, most importantly, the steps you can take to prevent and treat this debilitating condition.
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontitis, is an infection of the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It is caused by the buildup of plaque, which is a sticky film of bacteria on the teeth and gums. As plaque accumulates, it hardens into tartar and can only be removed by a dentist or dental hygienist. If not removed, the bacteria in plaque and tartar can cause inflammation of the gums, leading to gum disease.
In advanced stages, gum disease can cause damage to the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bones, and may result in tooth loss. It’s estimated that almost half of American adults over the age of 30 have some form of gum disease, making it one of the most prevalent oral health problems today.
What are The Symptoms of Gum Disease?
The symptoms that indicate there is a disease in your gums can vary depending on the stage of the condition. Some common signs include:
- Red or swollen gums
- Receding gums
- Bad breath
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pus between the teeth and gums
- Apparent changes in teeth alignment
It’s best to detect gum disease as early as possible. A visit to Durango Dental or your local dentist can determine the severity and the appropriate treatment for such a condition. Aside from an urgent check-up, you can also do the following to prevent it from getting worse.
1. Brush Your Teeth Twice A Day With Fluoride Toothpaste
Brushing teeth is the best way to remove plaque and prevent gum disease. Most toothpaste products contain fluoride, a mineral that helps strengthen the enamel on your teeth. This mineral makes your teeth more resistant to decay and gum disease.
You can remove plaque and bacteria from your teeth and gums by brushing twice daily. A toothbrush with soft bristles is essential, as stiff bristles can irritate the gums and cause further damage.
Brushing should be done in a gentle circular motion, paying particular attention to the gum line. That is where plaque is most likely to accumulate. By making toothbrushing part of your daily routine, you can maintain healthy gums and a beautiful smile for life.
2. Floss Daily
Flossing helps to remove food particles in between the teeth. It can reach the parts of the teeth a toothbrush cannot reach. This helps prevent the buildup of plaque, which can lead to gum disease and other oral health problems. When flossing, it’s essential to use a gentle sawing motion and to work the floss up and down the sides of each tooth. Be careful not to damage the gums. Flossing should be done once a day—ideally before bedtime—to remove plaque and bacteria that may have accumulated during the day.
3. Use Mouthwash
Mouthwash can help remove plaque, freshen your breath, and kill bacteria that can cause gum disease. There are many different types of mouthwash available. There is an antimicrobial mouthwash, which, as its name suggests, fights off bacteria. There is also fluoride mouthwash, which helps to strengthen the enamel on your teeth and protect it against decay.
Follow the label’s instructions when using mouthwash and swish it around your mouth for the recommended amount of time before spitting it out. It’s important to remember that mouthwash should not be used as a substitute for brushing and flossing but as an addition to a comprehensive oral hygiene routine.
4. Visit Your Dentist Regularly
Regular dental check-ups can help detect gum disease in its early stages when it is easier to treat. During a check-up, your dentist will examine your teeth and gums, look for signs of plaque or tartar buildup, and check for any changes in your mouth that may indicate the onset of gum disease.
Your dentist may use an X-ray machine to check for any signs of damage or decay. 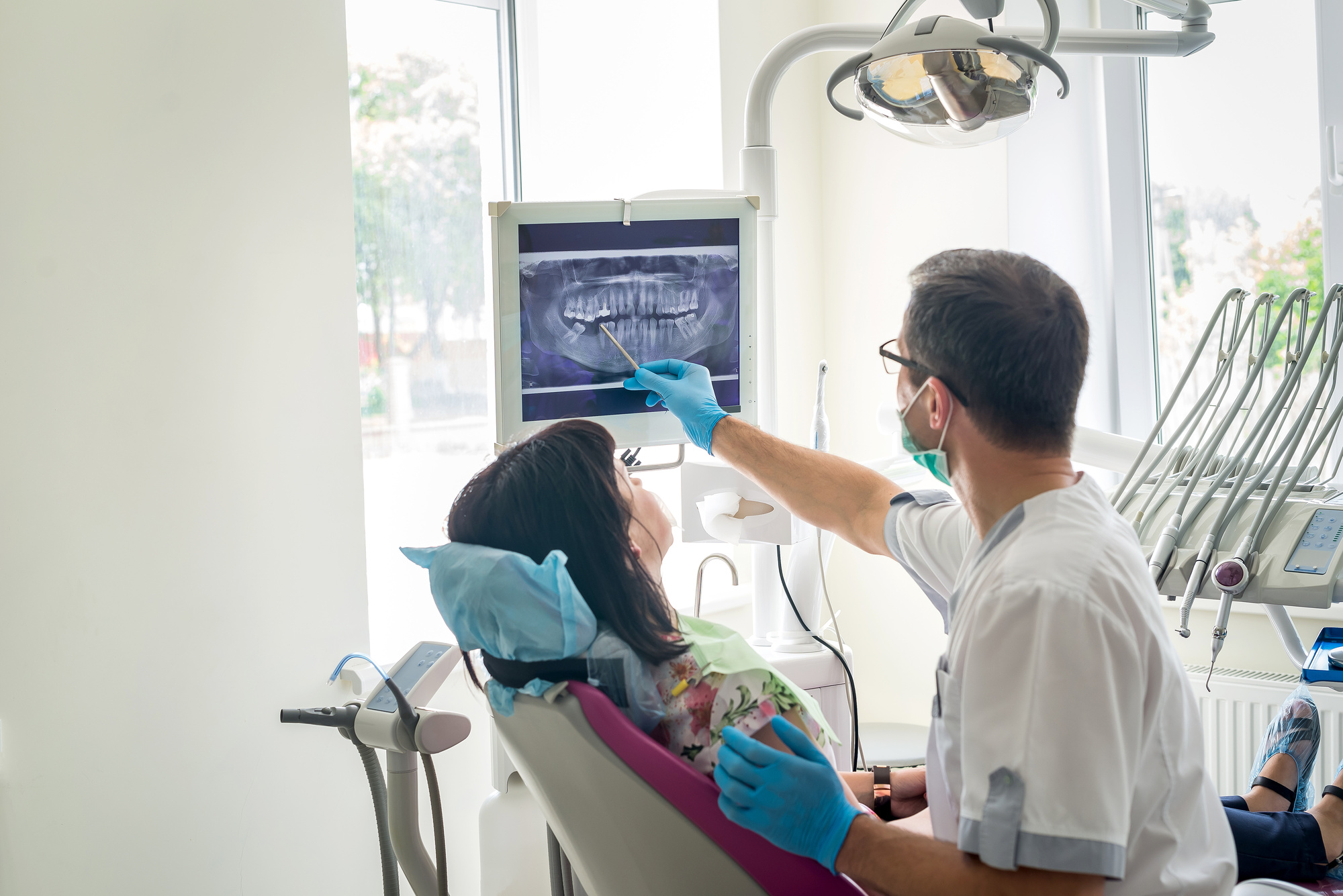 Based on their findings, they can recommend any necessary treatment, such as scaling and root planing, or refer you to a specialist. It’s recommended to see your dentist at least twice a year or more frequently if necessary.
Based on their findings, they can recommend any necessary treatment, such as scaling and root planing, or refer you to a specialist. It’s recommended to see your dentist at least twice a year or more frequently if necessary.
5. Stop Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease and has been shown to increase the risk of gum disease, reduce the effectiveness of treatment, and slow down the healing process. Smoking reduces blood flow to the gums, making it more challenging to receive the oxygen and nutrients they need to stay healthy.
Smoking also increases the production of harmful bacteria in the mouth, leading to plaque buildup. By quitting smoking, you can help improve the health of your gums, reduce your risk of gum disease, and improve your oral health.
6. Improve Your Diet
A diet high in sugar, processed foods, and carbohydrates can increase the risk of gum disease, as these foods can promote plaque buildup and the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth. On the other hand, a diet rich in nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, can help support your gums’ health and reduce your risk of gum disease. Therefore, it is vital to maintain a healthy diet as it significantly affects your overall oral health.
7. Treat Existing Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, make it more difficult for your gums to heal and increase your gum disease risk. Also, certain medications, such as those used to treat depression, can have a negative effect on gum health. If you have a medical condition, it’s essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to manage it effectively and prevent oral health complications brought about by other medications.
Treatments For Gum Disease
- Scaling– This involves deep cleaning the gums to remove plaque and tartar in the gums. Also known as root planing.
- Antibiotic therapy – Antibiotic medications, either topical or oral, can help control infection and promote healing of the gums.
- Gum surgery – In more advanced cases, gum surgery may be necessary to remove infected tissue and repair damage to the gums and supporting structures of the teeth.
- Lifestyle changes – Changing your diet and oral hygiene habits can help prevent gum disease from recurring.
- Medications – Anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce swelling and discomfort associated with gum disease.
- Laser therapy – Laser therapy can remove infected tissue and promote the healing of the gums.
Conclusion
Gum disease is a severe condition that can significantly impact your oral health and overall well-being. But, with proper care and attention, it is possible to prevent and treat gum disease and maintain healthy gums for life.
By taking these steps, you can help keep your gums healthy, avoid the discomfort and pain associated with gum disease, and enjoy a beautiful smile for years to come. Remember, the key to managing gum disease is early detection and treatment. Please don’t wait until it’s too late. Take control of your oral health today.








